Picture this: your employees are working diligently, but instead of solely using company-issued devices, they’re leveraging their own personal laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This is the essence of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), a practice that’s reshaping modern business operations.
Embracing BYOD helps with flexibility and productivity but also comes with new security challenges. Personal devices create potential vulnerabilities. Implementing a comprehensive BYOD security policy is essential. It protects your data and ensures smooth operations, allowing you to enjoy BYOD’s benefits while maintaining business integrity.
Key Takeaways
- Personal devices enhance efficiency and flexibility but require robust security policies.
- BYOD introduces risks like data breaches, malware, and lost devices, needing strict controls./li>
- BYOD policy needs defined device types, management, and data separation for secure integration.
- Use of MDM tools, encryption, and geo-fencing can ensure compliance and data protection.
- Clear BYOD policies on acceptable use, support, and data handling minimize risks and legal issues.
Defining Your Enterprise Mobility
In the long run, the specific term you use doesn’t really matter, they’re all part of the jargon surrounding enterprise mobility. What’s important is understanding what these terms mean for you, your users, and your company.
When comparing definitions, you’ll find a range from a very relaxed approach, where there is no mobility policy, to more structured integrations. This spectrum includes basic integration and access from personal smartphones (BYOD and CYOD) to more comprehensive control using company-owned and managed devices (COPE and COBO).
To define your own mobile program, whether it’s BYOD, CYOD, COPE, COBO, or another term, you need to outline three key elements clearly:
- The Device: What is it, who chooses it, and who covers the cost of the device and cellular service?
- Management and Support: Who manages the device and provides support?
- Integration and Applications: How integrated and essential is the device in daily workflows?
Physical Asset Management and Maintenance For BYOD

1. Policy and Compliance Essentials
Pro Tip: Survey employees to align policies with their needs.
- Tailor policies that fit your work culture, user habits, and legal requirements.
- Apply policies to everyone, including management, with clear permissions.
- Use Mobile Device Management for real-time compliance alerts on policy violations.
2. Data and Access Security
- Enforce encryption, passwords, and limit access to cameras or microphones.
- Keep corporate and personal data distinct to protect user privacy.
- Mandate robust passwords and promote biometric authentication for extra security.
- Restrict data access outside defined areas by tracking device locations.
3. Device Maintenance and Updates
- Schedule routine cleaning to remove dust and debris, checking for physical damage.
- Encourage employees to apply the latest software patches and firmware updates. Example: Set reminders for quarterly updates.
- Enable remote wipe capabilities to secure data if devices are lost or stolen.
4. Inventory and Storage Solutions
- Maintain an up-to-date inventory to monitor usage and status.
- Offer lockers or cabinets for safe device storage in shared workspaces.
- Block inappropriate apps/sites and set data access limits for efficiency.
Defining a BYOD Security Policy
1. BYOD Policy Elements
- Acceptable Use: Specify permitted applications and assets on personal devices.
- Minimum Security Controls: Outline required security measure for devices.
- Company-Provided Components: Provide SSL certificates for device authentication.
- Company Rights: Include rights for altering devices, such as remote wiping for lost or stolen devices.
- Permissible Device Types and Security Policy: Specify allowed device types and establish a stringent security policy.
- Motivate employees to use security features like device locking and passwords through clear policies.
2. Service Policies for BYOD Devices
- Outline IT support for connecting to the company network and resolving application conflicts.
- Define support for applications installed on personal devices.
- Ownership, Reimbursement, and Security Requirements: Clarify ownership of apps and data, permitted/prohibited applications, and reimbursement policies.
- Specify security requirements for BYOD devices, including mobile security application installation.
3. Employee Exits and Data Handling
- Define procedures for handling company data on devices when employees leave the company.
- Explain policies for wiping employee devices and IT responsibilities during employee separations.
- Risks, Liabilities, and Disclaimers: Disclose company liability for personal data and employee liability for data breaches.
- Include disclaimers and risks associated with BYOD in written policies.
BYOD Security Challenges
BYOD security is difficult for enterprises and SMBs since it requires controlling employees’ personal devices.
- Data Security: Protecting company data on personal devices from unauthorized access or data leaks.
- Device Management: Ensuring devices comply with security policies, software updates, and remote wipe capabilities.
- Network Security: Preventing unauthorized access to company networks through a BYOD device.
- Malware and Virus Risks: Mitigating the risk of malware infections or virus attacks from personal devices.
- Lost or Stolen Devices: Managing the security implications of lost or stolen devices containing sensitive company information.
- Employee Education: Ensuring employees understand and follow security protocols to reduce BYOD-related risks.
- Legal and Compliance Issues: Addressing regulatory requirements and legal implications of BYOD security breaches.
Security Solutions For BYOD
Protecting personal devices in BYOD program is non-negotiable to protect company’s data. Here’s a breakdown of proven security solutions to keep your BYOD setup secure while empowering employees.
1. Employee Training and Awareness
- Train employees regularly on acceptable use and data security hygiene. Pro Tip: Host quarterly webinars to reinforce best practices.
- Set clear rules that secure devices without stifling personal use.
2. Data Protection Measures
- Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit to block theft or interception.
- Require robust passwords and encryption throughout the data lifecycle.
- Install antivirus on all BYOD devices to combat malware and viruses.
3. Device and App Management
- Deploy MDM to centrally secure, monitor, and manage devices. Example: Use MDM to push updates instantly.
- Segregate work data in a secure environment, allowing personal use outside it.
- Use device/OS controls to manage app installations.
- Block high-risk or distracting apps to boost productivity.
- Permit only pre-approved, safe apps for secure access.
4. Monitoring and Response
- Implement systems to detect unusual activity or locate lost devices.
- Combine context-aware solutions to control user access, apps, networks, and devices while keeping encryption active.
Difference Between BYOD, CYOD, COBO and COPE

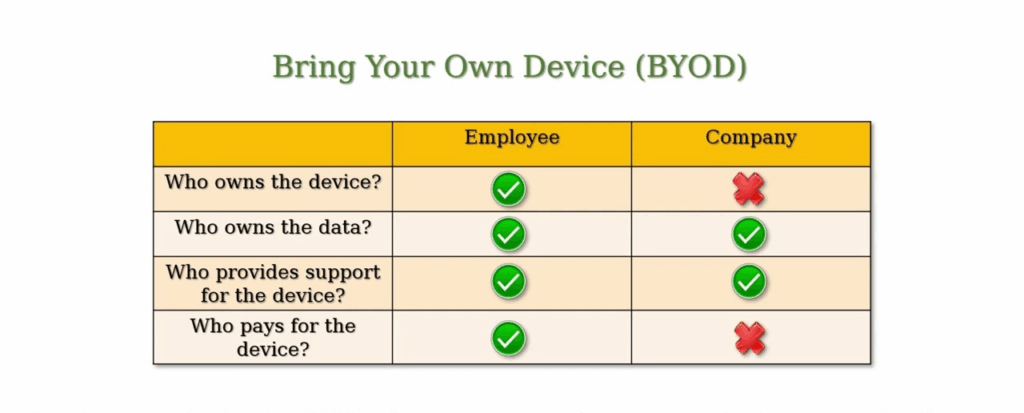
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)
- Device Ownership: Personal devices owned by employees.
- Management: Typically looser device management and support.
- Integration: Limited network access and less emphasis on enterprise applications to balance security risk.
- User Freedom: High, as employees use their own devices.
- Cost: Costs are primarily borne by employees, with some potential reimbursements by the company.
CYOD (Choose Your Own Device)
- Device Ownership: Employees can benefit from dedicated device e-ordering from a pre-approved list.
- Management: Moderate level of management and support by the company.
- Integration: Devices are more integrated into corporate systems compared to BYOD.
- User Freedom: Medium, as choices are limited to the approved list.
- Cost: The company typically covers device and connectivity costs.
COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled)
- Device Ownership: Devices are company-owned.
- Management: High level of management and support, with usage controls.
- Integration: Devices are tightly integrated with corporate applications and systems.
- User Freedom: Users can perform basic personal tasks (calls, messaging, personal apps) under certain controls.
- Cost: The company covers all costs related to the device and connectivity.
COBO (Corporate-Owned, Business Only)
- Device Ownership: Devices are company-owned.
- Management: Very high level of management and support with strict usage policies.
- Integration: Devices are used exclusively for business purposes and are tightly integrated with corporate systems.
- User Freedom: Very low, as personal use is prohibited.
- Cost: The company covers all costs related to the device and connectivity.
BYOD Pros
There are a ton of advantages to implementing BYOD policies.
- Employees using their own devices work more efficiently due to familiarity, leading to faster adoption and fewer technical issues. This also reduces training time and increases motivation, as employees feel more invested in their work.
- With BYOD, no additional training is required since employees are already familiar with their devices. This saves time and money on training sessions, allowing employees to start tasks immediately.
- BYOD cuts costs by eliminating the need to purchase and maintain company-issued devices. A comprehensive BYOD program can save up to $3,150 per employee per year. Additionally, employees can choose devices that best suit their needs, boosting productivity.
- Employees can access the latest technology without relying on potentially outdated company-provided devices, increasing engagement and motivation while saving on equipment costs.
- Allowing employees to use their personal devices improves job satisfaction and ownership, leading to better performance and productivity. BYOD can also reduce turnover by giving employees more control over their work life. A Salesforce report shows companies could gain up to 240 hours per year by adopting a BYOD policy.
BYOD Cons
Implementing BYOD policies can pose some serious complexities if not implemented properly.

- BYOD can pose significant security risks like personal devices often lack the robust protection of corporate-owned ones, and employees may use weak or reused passwords. Additionally, connecting to unsecured public Wi-Fi networks and storing sensitive data without encryption increase vulnerability to data breaches, theft, and loss.
- BYOD can lead to support challenges, as IT staff must manage a wide range of devices and operating systems. This diversity can frustrate both employees and IT teams.
- Compatibility can be problematic with BYOD. Different devices have varying operating systems, software versions, and screen sizes, making it difficult to develop applications that work universally. Employees changing devices frequently compounds this issue.
- BYOD introduces legal, privacy, and security concerns. Policies must clearly outline expectations for using company data, including retention, sharing, access, and deletion. Additionally, they must specify consequences for misuse or unauthorized access to company information.
- Retrieving data from personal devices can be difficult if something goes wrong. Employee-owned devices are less controlled than company-owned ones, complicating remote data wiping and troubleshooting. Employees may also be hesitant to hand over personal devices for inspection, necessitating additional security measures to protect corporate data.
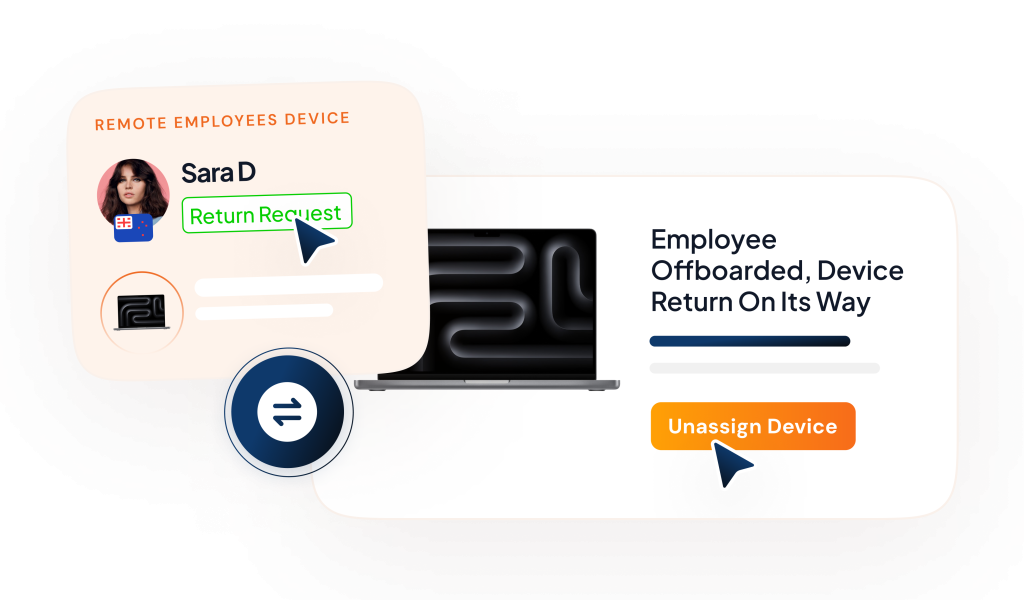
Should you provide a company laptop to your remote workers?
Knowing that there are different methods of device management whether employees use their own or company provided. And yet, you might wonder if it’s worth providing company-owned equipment for remote work. Although the answer depends on your specific needs, we highly recommend to provide corporate device for remote employees.
One of the main reasons for this approach is BYD security challenges. With remote work, there’s less oversight of how employees use their devices. By giving employees company-owned laptops, your organization can maintain access to the machines, allowing your IT team to remotely manage and troubleshoot any issues that arise. This level of control is necessary for maintaining the integrity and security of your company’s network and data.
Additionally, when employees leave your organization, you can retrieve the device and redeploy it for a new user. This can help your company make the most of the equipment throughout its useful life and even save costs in procurement. You can also make sure that your data stays safe by remotely wiping the device when the employee leaves or in case there are issues with the retrieval.
Overcoming BYOD Security Risks
Unduit’s BYOD security services ensure compliance and protection for employee-owned devices in complex mobile environments. Our platform delivers robust security without compromising 24/7 accessibility.
Key Features
- Real-Time Threat Detection with agent-based monitoring provides instant alerts for unauthorized changes at the device level.
- Providing comprehensive compliance that aligns with PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and more, with automated audit-ready reporting.
- Quickly reverse harmful changes to maintain device integrity and security.
- One intuitive tool for monitoring, managing, and auditing BYOD devices globally.
Unduit empowers your workforce with secure, flexible BYOD access while safeguarding sensitive data. Schedule a demo to strengthen your mobile security today
Frequently Asked Questions
What is BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)?
BYOD refers to the practice of employees using their personal devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, for work purposes.
Why is BYOD important?
BYOD is important as it allows employees to work more efficiently with devices they are familiar with, reduces training time and costs, and can lead to cost savings for the company.
When should a company consider implementing a BYOD policy?
A company should consider implementing a BYOD policy when it wants to leverage employee familiarity with personal devices, increase productivity, and potentially reduce device-related costs.
How does BYOD differ from other mobility programs like CYOD, COBO, and COPE?
BYOD involves employees using their personal devices, while CYOD (Choose Your Own Device) allows employees to choose from a list of company-owned devices. COBO (Corporate-Owned, Business Only) provides company-owned devices for exclusive business use, and COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled) allows personal use within certain controls on company-owned devices.
What are the benefits of implementing a BYOD policy?
Benefits of BYOD include increased efficiency, reduced training costs, potential cost savings, improved employee satisfaction, and flexibility in device choice.
What are the challenges associated with BYOD?
Challenges of BYOD include security risks, device management complexities, compatibility issues, legal and privacy concerns, and data retrieval difficulties.
How can a company address the security risks of BYOD?
Companies can address BYOD security risks through employee education, encryption, strong passwords, application control, mobile device management (MDM), containerization, blacklisting/whitelisting, antivirus software, monitoring systems, and a multi-faceted security approach.
Why is defining a BYOD security policy important?
Defining a BYOD security policy is important to establish guidelines for acceptable use, minimum security controls, company-provided components, employee exits and data handling, risks, liabilities, disclaimers, and service policies for BYOD devices.
How can companies mitigate the challenges of BYOD policies?
Companies can mitigate BYOD challenges through effective security solutions, employee education, encryption, strong passwords, application control, mobile device management (MDM), containerization, blacklisting/whitelisting, antivirus software, monitoring systems, and a multi-faceted security approach.
What encryption methods are commonly used to secure data on BYOD devices?
Common encryption methods used to secure data on BYOD devices include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman).
What is containerization, and how does it enhance security in BYOD environments?
Containerization is a technology that separates work-related data from personal data on a device, creating a secure environment for corporate information. It enhances security in BYOD environments by preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data and allowing IT teams to manage and secure corporate data independently of personal data.
What are some common mobile device management (MDM) solutions used for BYOD security?
Common MDM solutions used for BYOD security include VMware Workspace ONE, Microsoft Intune, Citrix Endpoint Management, and IBM MaaS360. These solutions help manage and secure mobile devices, enforce security policies, and monitor device compliance.
How can companies monitor and track BYOD devices for security purposes?
Companies can monitor and track BYOD devices for security purposes using MDM solutions that provide real-time monitoring, device tracking, and alerts for policy violations. Additionally, companies can implement network monitoring tools to detect unauthorized access attempts from BYOD devices.